Remote Patient Monitoring Implementation: Trends and Key Challenges
Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting remote patient monitoring (RPM) to enhance care management for patients outside of traditional hospital settings. They are implementing various programs nationwide that utilize digital health tools, wearables, smart home technology, and telehealth to establish connections between patients and care teams. These initiatives aim to improve patient monitoring and enable more effective healthcare delivery beyond the confines of hospitals.
According to Business Insider, approximately 30 million patients in the United States are expected to adopt remote patient monitoring solutions by 2024. A recent survey conducted by MSI International in 2021 revealed that 80% of the US population has a favorable attitude towards remote patient monitoring, with 50% expressing the desire to see it integrated into their medical care.
What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
RPM, is subcategory of telehealth, enabling patients to utilize mobile medical devices and technology for gathering patient-generated health data (PGHD) which is then transmitted to healthcare professionals. Physicians can utilize the collected data for diagnostics and continuous monitoring of patients' health status. By doing so, RPM enables healthcare professionals to provide guidance on health and well-being and make adjustments to medication type or dosage based on the results.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is commonly employed to support individuals in need of chronic, post-discharge, or senior care. By establishing a connection between high-risk patients and remote monitoring systems, RPM enables healthcare organizations to receive alerts about potential health issues and facilitates the continuous tracking of patient data even between in-person visits.
How Remote Patient Monitoring Works?
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) utilizes various components, although they may differ based on the device or condition being monitored. A key component is a wireless sensor-patient mobile app capable of measuring specific physiological parameters and storing the collected data. This storage system should also facilitate connectivity with other sensors, healthcare provider databases, and related applications. Applications commonly offer users an interface to track, analyze, and receive treatment recommendations based on the data.
Related: FHIR Implementation for Interoperability Success in Healthcare
-
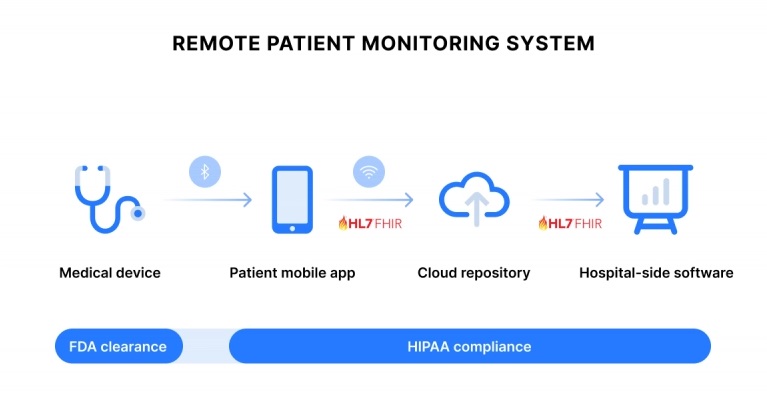
Remote Patient Monitoring System
The remote patient monitoring system facilitates the connection between a medical device that collects health data and transmits it to healthcare providers. Only wireless, non-invasive tools authorized by the FDA, such as electronic thermometers and cardiac monitors, are used for remote patient management.
-
Patient Mobile App
The patient mobile app plays a crucial role in gathering data from wearables and sensors and transmitting it to healthcare staff. It must comply with strict criteria, including HIPAA regulations, support for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for data exchange, and secure API integrations. Additionally, it can provide data visualization, educational resources, reminders, and communication channels for patients to connect with their doctors.
-
Cloud Repository
In today's healthcare system, patient-doctor conversations and qualitative data play a significant role. However, the integration of big data in connected healthcare connects various areas of the healthcare space, empowering physicians to make more accurate predictions and determine the best course of action for their patients. By leveraging comprehensive data and analytics, doctors can make confident decisions while minimizing clinician errors.
-
Hospital Web Application
The hospital web application, compliant with HIPAA requirements, handles electronic health information and integrates with the hospital's Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system and the remote patient monitoring web platform using FHIR-based APIs for enhanced interoperability. It often includes modules for decision support, reporting, notifications, and analytics, which also make the hospital system compliant with the ONC Cures Act.
-
Sensors or Smart Connected Devices for Patient Monitoring
Sensors or smart connected devices are used to gather patient vitals, such as body temperature and blood pressure, and transmit them to the cloud RPM server for further analysis. These devices communicate with the patient tracking software, enabling remote monitoring of patients' health.
Trends in Remote Patient Monitoring
The trends in Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) include the widespread adoption of wearable devices for continuous monitoring, integration with telehealth platforms for remote consultations, and the utilization of AI and data analytics for personalized insights and predictive healthcare. These trends aim to enhance patient care, improve health outcomes, and increase access to healthcare services.
Remote Patient Monitoring Software Types:
-
Telehealth Solutions
Enable remote communication between patients and practitioners through features like file exchange, teleconferencing, and instant messaging. Used in various medical fields.
-
IoMT-Based Applications
Use medical devices on smartphones or embedded in devices to monitor patient health metrics via IoT technology.
-
Electronic Data Capture Solutions
Capture health conditions and subjective feelings remotely, such as pain levels.
-
IoT Medical Applications
Enable remote monitoring of vital health information, such as heart rate and glucose levels, through compatibility with wearable medical devices.
-
Questionnaire Applications
Allow patients to respond to questionnaires remotely, particularly useful for tracking mental illnesses and depression.
-
Video Conferencing Applications
Facilitate remote healthcare consultations, examinations, and prescription management through video conferencing, with the potential to incorporate features like queue management and electronic medical records.
-
Precision Medicine Solutions
Anonymize and analyze health data from participants for research purposes, providing valuable insights into personalized medicine.
Related: Unlocking Connect Health Potential with Interoperability
Remote Patient Monitoring Device Types:
-
Cardiac Monitoring Devices
Provide real-time information on heart rate, aiding in early detection of heart-related issues.
-
Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices
Track glucose fluctuations and enable sharing with doctors for diabetes management.
-
Hand Hygiene Monitoring Systems
Provide information on hygiene practices beyond hand hygiene.
-
Depression and Mood Monitoring Devices
Monitor physiological parameters associated with mood swings to aid in detecting depression symptoms.
-
Technologies for COPD and Asthma
Assist individuals with reminders for medication usage and track attack frequency and triggers.
-
Pregnancy Monitoring Systems
Collect vital data on the health of pregnant women and their unborn children.
-
Sensors for Digestive Systems
Use ingestible sensors to detect internal bleeding or indicate stomach pH levels.
What are the Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) for Patients
-
Convenience
RPM allows patients to monitor their health from the comfort of their own homes, reducing the need for frequent visits to healthcare facilities. It eliminates the inconvenience and time spent on travel, waiting rooms, and scheduling appointments.
-
Improved Access to Care
RPM bridges the gap between patients and healthcare providers, enabling timely access to care. Patients can receive continuous monitoring and support, especially in remote or underserved areas where access to healthcare services may be limited.
-
Early Detection of Health Issues
With RPM, patients' vital signs and health data are continuously monitored, allowing for early detection of any changes or abnormalities. This early detection can lead to prompt medical intervention, preventing the progression of health conditions and reducing the risk of complications.
-
Personalized and Proactive Care
RPM enables healthcare providers to personalize treatment plans based on real-time patient data. Providers can make timely adjustments to medications, therapies, or lifestyle recommendations to optimize patient outcomes. This proactive approach to care can result in better management of chronic conditions and improved overall health.
-
Increased Patient Engagement
RPM empowers patients to actively participate in managing their health. By monitoring their own data, patients gain a better understanding of their conditions, making them more engaged in their own care. This can lead to increased adherence to treatment plans and healthier lifestyle choices.
-
Peace of Mind
RPM provides patients and their families with peace of mind, knowing that their health is being continuously monitored. Patients feel reassured knowing that healthcare providers are keeping a close eye on their well-being and are ready to intervene if necessary.
-
Cost Savings
RPM has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by minimizing hospital readmissions, emergency room visits, and unnecessary outpatient appointments. It promotes early intervention, preventing complications that could result in more expensive treatments or hospitalizations.
How Remote Patient Monitoring benefits Healthcare providers?
Remote patient monitoring software development brings several advantages to healthcare providers. One key benefit is cost efficiency, as it can lead to savings of up to $6,500 per patient per year and potentially save the US healthcare system billions of dollars annually. By implementing remote monitoring, healthcare businesses can reduce the number of in-hospital appointments and human operated processes, thereby lightening the workload of hospital staff and reducing labor and equipment upkeep budgets.
Fewer Readmissions
Building a patient tracking system in hospitals can lead to better patient outcomes, including a 5% reduction in patient readmissions. Documented cases, such as the Cloud DX's Connected Health Kit source, show that virtual care through remote patient monitoring can prevent and resolve more medication errors during care transitions, resulting in fewer readmissions and less pain reported by patients.
Additionally, remote tracking using patients' own devices lessens the burden on healthcare professionals and their equipment. Overall, remote patient monitoring software development offers cost savings and operational efficiency for healthcare businesses.
What are the Challenges in Remote patient Monitoring
Patient Data Security
The security of remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a significant concern as it involves transmitting sensitive medical data over the internet. RPM systems are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, data breaches, and other threats that can compromise the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of patient information. To address these issues, robust security measures, such as encryption techniques like elliptic curve cryptography, should be implemented to safeguard communication and ensure the privacy and security of patient data.
RELATED: Tips for Securing Private Health Data in Healthcare Cyber security
Data Accuracy in RPM
Ensuring the accuracy of data transmitted through RPM systems is crucial for making reliable medical assessments and decisions. Various factors can affect data accuracy, including the quality and calibration of sensors used in monitoring devices. It is essential to use high-quality sensors that provide accurate measurements and ensure proper calibration to minimize the risk of erroneous data that could lead to incorrect diagnoses or treatment decisions.
Real-time Data Access in RPM
Real-time access to patient data is essential for timely monitoring and intervention in critical situations. Healthcare professionals need to be able to access up-to-date patient data to assess their condition and provide appropriate care. However, ensuring real-time data access poses challenges, such as maintaining constant connectivity between devices and the central monitoring system. Adequate network infrastructure and bandwidth are required to support the seamless transmission of data in real time.
System Integration
System integration is crucial for effective RPM implementation, especially when different healthcare providers and systems are involved, and challenges can arise due to the diversity of software and hardware used in healthcare settings. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability between various systems and devices, including leveraging the FHIR standard for integration, is essential to enable seamless data exchange and integration. Additionally, integrating RPM into existing healthcare workflows and ensuring patient compliance with the monitoring system are important considerations for successful implementation.
The Cost of RPM
Implementing RPM in the healthcare industry incurs costs that need to be carefully managed. These costs include acquiring monitoring devices, licensing fees for software, maintenance and technical support, and staff training. Adequate budget planning is necessary to cover these expenses and ensure the sustainable implementation and operation of RPM systems.
By addressing the security concerns, ensuring data accuracy, enabling real-time data access, promoting system integration, and managing the costs effectively, remote patient monitoring has the potential to enhance patient care, improve healthcare outcomes, and optimize resource utilization in the healthcare industry.
How can Tech companies encourage RPM adoption?
Partnering with the right healthcare IT company is essential for successful implementation of remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions. At KPi-Tech, we simplify the RPM process with EHR integration , and provide training and support for healthcare providers. Our expertise in application development and interoperability ensures seamless integration and improved care coordination. With experience in delivering HIPAA-compliant solutions, including telemedicine and cloud-based platforms, we are your trusted technology partner.
Contact us today to revolutionize your healthcare practice with remote patient monitoring.




